Từ FW v59.00.502 trở lên, CMU bị khóa và người dùng không thể truy cập vào hệ thống của riêng họ và không thể cài đặt các chỉnh sửa nữa.
Hiện tại cách duy nhất để phá vỡ điều này là tạo một kết nối nối tiếp và làm theo các hướng dẫn rất cẩn thận.
Quá trình này sẽ cho phép bạn chạy các tinh chỉnh từ USB.
*** Thiết Bị Cần Thiết:
- Bộ chuyển đổi nối tiếp USB sang TTL (Bất kỳ mô-đun CP2102 nào khác cũng sẽ hoạt động. Các bộ điều hợp USB-TTL khác cũng có thể hoạt động.)

- Ổ đĩa flash USB
- Khóa 10 mm với bộ mở rộng

- Putty hoặc SecureCRT
- Mazda AIO Tweaks
Chuẩn bị:
Ổ đĩa flash USB:
Phương pháp AIO của MZD:
- Định dạng ổ đĩa sang FAT32
- Sử dụng MZD-AIO v2.7.9 +: Chạy Hồi Autorun & Recovery Hồi sinh với Phục hồi qua kết nối nối tiếp Cài đặt ID &7 Cài đặt ID_7 Recovery ScScript Gói tùy chọn
- AIO sẽ tạo Thư mục ‘XX’ và các tệp cần thiết trong thư mục _copy_to_usb
- AIO sẽ đề nghị sao chép tệp trực tiếp vào Ổ USB được kết nối
Phương pháp thủ công:
- Định dạng ổ đĩa sang FAT32
- Tạo thư mục có tên ‘XX’
- Thêm nội dung của kho lưu trữ này vào thư mục ‘XX’
- Nếu bạn muốn chiếc xe tự tạo Điểm truy cập Wifi, hãy định cấu hình trong tệp
XX/00-start-wifiAP/wifiAP.config. Nếu không, hãy xóa thư mục 00-start-wifiAP. Nếu bạn muốn xóa Wifi AP sau khi cài đặt xong, hãy sao chép nội dung của Wifi Uninstall Script vào ổ đĩa flash và kết nối với CMU.
- (Tùy chọn) Sử dụng AIO để cài đặt một số tinh chỉnh đã chọn trên cùng ổ flash USB để chạy sau khi hoàn thành.
Xem video sau để xem cách kết nối để root mazda connect
Thực hiện:
- Mở hộp găng tay
- Gỡ nẹp trang trí. Bạn sẽ cần phải sử dụng nhiều lực hơn bạn mong đợi. Khu vực quạt phía trước được gắn vào trang trí và cũng sẽ tắt.
- Ngắt kết nối cáp đèn cảnh báo nguy hiểm
- Sử dụng cờ lê ổ cắm 10 mm để tháo bu-lông

- Headunit sẽ trượt ra về phía bạn
Nối CMU (Mazda connect) vào usb đến máy tính laptop
Không sửa đổi bất kỳ lệnh nào dưới đây Nếu các lệnh không hoạt động, thì bạn đã làm sai điều gì đó (tức là bạn chưa đăng nhập hoặc dây RX / TX không được nối dây đúng cách)
- Bạn sẽ cần phải có 3 dây kết nối với CMU: Transmit (TX), Nhận (RX) và Ground (GND)
- Dưới đây là hình ảnh mặt sau của CMU. Chúng tôi sẽ thêm cáp vào đầu nối ‘power & more’. Dưới đây là hình ảnh chi tiết hơn về nơi cáp RX và TX đi.
-
- Hãy chắc chắn rằng cáp đang đi vào cổng. Nó phải đi trong khoảng một inch. Cáp GND có thể đi bất cứ nơi nào miễn là nó chạm vào CMU. Tôi khuyên bạn nên tháo nhẹ một trong các ốc vít đầu Philips và nêm cáp vào đó.
- Kết nối đầu kia của dây với mô đun CP2102 trong cổng tương ứng.
Ứng dụng Bảng điều khiển nối tiếp:
- Đảm bảo bạn biết lệnh dán là gì cho ứng dụng Bảng điều khiển nối tiếp của bạn. Trong Putty, bạn nhấp chuột phải vào bên trong cửa sổ terminal và nó sẽ dán bất kỳ lệnh nào bạn đã sao chép. Đối với SecureCRT, bạn nhấn Ctrl + Shift + V để dán.
- Windows sẽ tự động gán Cổng COM cho mô-đun CP2102 sau khi được cắm. Đi đến Trình quản lý thiết bị> Cổng (COM & LPT) để xem Cổng COM # là gì
- Đối với SecureCRT, trong Tùy chọn> Kết nối> Nối tiếp, đặt Cổng = COM #, Baud = 115200, Bits dữ liệu = 8, Parity = Không, Dừng Bits = 1
- Đối với Putty, bạn chỉ cần chọn ‘Nối tiếp’ và sau đó nhập Cổng COM # và đặt Baud thành 115200
- Bạn nên bắt đầu xem cuộn văn bản ngay cả khi xe đã tắt
- Cắm ổ đĩa flash
- Bật xe sang chế độ ACC bằng cách chỉ cần nhấn nút Bật mà không cần đạp chân để bật hoàn toàn xe
- Bây giờ bạn thực sự sẽ thấy văn bản bay qua, hãy nhớ rằng các lệnh đang hoạt động mặc dù bạn không thể thấy những gì bạn đang gõ vì văn bản bay qua.
- Nhấn Enter in terminal và CMU sẽ trả lời với ‘đăng nhập’. Đối với một số bước tiếp theo, đảm bảo bạn không mắc lỗi chính tả nào. Có lẽ tốt nhất là sao chép và dán các lệnh (để dán bạn chỉ cần nhấp chuột phải vào cửa sổ terminal).
- Nếu văn bản bay quá nhanh, có vẻ như bạn không thể nhập chính xác mọi thứ, hãy sao chép và dán từng lệnh và nhấn enter! Có vẻ như các lệnh của bạn không được gửi tới Mazda nhưng đừng lo lắng ( với điều kiện là hệ thống dây của bạn đúng. Nếu bạn có mô-đun có đèn LED, bạn có thể kiểm tra TX là Truyền / RX là Nhận )
- Khởi động lại Mazda CMU bằng cách giữ nút Nav + Mute trong hơn 10 giây.
- Đầu vào
và nhấn Enter Copy - Đầu vào
và nhấn Enter Copy
Chú ý: Sau khi cài đặt các script autorun bạn sẽ có thể đăng nhập như là người dùng root với username: CMU pass: JCI
- Chạy
-
- (Tùy chọn) Để kiểm tra xem các tệp đã được di chuyển vào thư mục chưa, hãy chạy
-
- Các tập tin / thư mục nên được tô màu xanh lục / xanh lam vì chúng là các thư mục / thực thi. Bạn có thể phải chạy nó vài lần để xem đầu ra của Bảng điều khiển nối tiếp.

-
- Hủy bỏ ổ đĩa flash, tắt xe, chèn ổ đĩa flash đã cài đặt tinh chỉnh AIO, bật xe trở lại trong chế độ ACC
- Sau vài phút, bạn sẽ thấy một thông báo cho biết các mod đang được cài đặt. Quá trình này có thể mất khoảng 2 – 20 phút.
Kết thúc
- Bây giờ mọi thứ đã được cài đặt, bạn có thể đặt mọi thứ lại với nhau
- Tháo dây TX, RX, GND
- Trượt CMU trở lại
- Gắn bu lông bằng cờ lê ổ cắm 10 mm
- Kết nối cáp kết nối ánh sáng nguy hiểm để cắt
- Đẩy lùi
- Từ đây trở đi, bạn chỉ cần sử dụng flashdrive để cài đặt các chỉnh sửa
- Chạy
 Công Ty TNHH TM Công Nghệ Suntek Chuyên Camera Giám Sát, Mạng không dây, không ổ cứng, bootrom game server NXD
Công Ty TNHH TM Công Nghệ Suntek Chuyên Camera Giám Sát, Mạng không dây, không ổ cứng, bootrom game server NXD
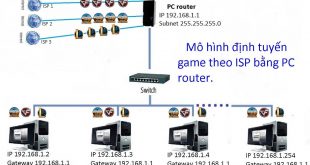



Philosophy is the discipline that studies fundamental and universal questions, such as existence, knowledge, values, mind, and language. It covers a vast number of topics and problems, ranging from ethics and politicians to metaphysics and logic. Here are the main nuances of philosophy:
1. Definition of Philosophy
Philosophy comes from the Greek words “philos” (love) and “sophia” (wisdom). It is the desire to understand and make sense of the world around us and our place in it.
2. The Main branches of philosophy
– Ontology research of the essence of being and existence.
– Epistemology the study of the nature and limits of knowledge.
– Ethics the analysis of moral principles and concepts of good deed and evil.
– Logic research of the forms and principles of correct thinking.
– Socio-political philosophy the study of questions of power, justice and the state.
3. Notable Philosophers
Throughout the history of philosophy, almost many thinkers have made meaningful contributions to this science. Some of the most recognizable include:
– Socrates, considered the progenitor of Western philosophy.
– Plato, a student of Socrates, developed the doctrine of forms.
– Aristotle, the creator of logic and a large number of scientific fields.
– Immanuel Kant, known for his own Philosophy critical philosophy and work on moral issues.
4. The Relevance of Philosophy in the Modern World
Philosophy remains urgent in the modern world since enables people to understand complex social and ethical issues, also develops critical thinking. It influences the legal system, politicians, and various fields of science.
5. Practical Applications of Philosophy
Philosophical ideas penetrate daily life. Ethical reflection helps people do the correct thing in difficult situations, and philosophical analysis contributes to best understanding of problems related to technology, art, and social justice.
Philosophy is not only an academic discipline, as well as method of thinking assists us to understand life’s complexities and make informed choices.
Philosophy is the discipline that studies fundamental and universal questions, including existence, cognition, values, mind, and language. It covers a vast number of subjects and issues, from ethics and political figures to metaphysics and logic. Here are the main aspects of philosophy:
1. Definition of Philosophy
Philosophy comes from the Greek words “philos” (love) and “sophia” (wisdom). It is the desire to understand and make sense of the world around us and our place in it.
2. The Main branches of philosophy
– Ontology research of the essence of being and existence.
– Epistemology the study of the nature and limits of knowledge.
– Ethics the analysis of ethical principles and concepts of good and evil.
– Logic research of the forms and principles of correct thinking.
– Socio-political philosophy the study of questions of power, justice and the state.
3. Famous Philosophers
In the course of the history of philosophy, many thinkers have made weighty contributions to this science. Some of the most famous include:
– Socrates, considered the founder of Western philosophy.
– Plato, a pupil of Socrates, developed the doctrine of forms.
– Aristotle, the creator of logic and a huge number of scientific fields.
– Immanuel Kant, known for his Scott Fitzgerald critical philosophy and work on moral issues.
4. The Relevance of Philosophy in the Modern World
Philosophy remains urgent in the modern world as it helps people to understand difficult social and ethical issues, and also develops critical thinking. It affects the legal system, politicians, and different fields of science.
5. Practical Applications of Philosophy
Philosophical ideas enter daily life. Ethical reflection helps people do the right thing in difficult situations, and philosophical analysis contributes to most excellent understanding of issues related to technology, art, and social justice.
Philosophy is not only an academic discipline, yes and method of thinking that helps us to understand life’s complexities and make informed choices.
Philosophy is the discipline that studies major and universal questions, including existence, cognition, values, mind, and language. It covers a vast number of subjects and issues, from ethics and political figures to metaphysics and logic. Here are the main aspects of philosophy:
1. Definition of Philosophy
Philosophy comes from the Greek words “philos” (love) and “sophia” (wisdom). It is the desire to understand and make sense of the world around us and our place in it.
2. The Main branches of philosophy
– Ontology research of the essence of being and existence.
– Epistemology the study of the nature and limits of cognition.
– Ethics the analysis of moral principles and concepts of good deed and evil.
– Logic research of the forms and principles of correct thinking.
– Political philosophy the study of questions of power, justice and the state.
3. Eminent Philosophers
During the history of philosophy, almost many thinkers have made significant contributions to this science. Some of the most famous include:
– Socrates, considered the founder of Western philosophy.
– Plato, a student of Socrates, developed the doctrine of forms.
– Aristotle, the creator of logic and a large number of scientific fields.
– Immanuel Kant, known for his Marcel Proust critical philosophy and work on moral issues.
4. The Relevance of Philosophy in the Modern World
Philosophy remains relevant in the modern world because it helps people to understand complex social and moral issues, and also develops critical thinking. It affects the legal system, politicians, and different fields of science.
5. Practical Applications of Philosophy
Philosophical ideas penetrate daily life. Ethical reflection helps people do the correct thing in difficult situations, and philosophical analysis contributes to most excellent understanding of problems related to technology, art, and social justice.
Philosophy is not only an academic discipline, yes and method of thinking that helps us to understand life’s complexities and make informed choices.